As part of T137783, this ticket explores the idea of filtering the general stream of contributions for the purpose of reviewing them. This can be supported by either improving the current recent changes page, or by providing a dedicated view.
Goals
- Allow exploration of changes. Provide an overview of the contributions to review, surfacing relevant information about the changes and the users for reviewers to act on them.
- Adapt to the reviewing task. Allow users to customise the contributions they want to focus on according to the task at hand (e.g., helping new users vs. fighting vandalism).
Scenarios
- Daily review. Adriana reviews the changes by good-faith newcomers making positive contributions to thank some of them. Then switches to check good-faith newcomers making damaging contributions, in order to help editors improve their edits. She is able to identify the changes more more critical to be reviewed, as well as getting a general idea of what was changed and who was making such change.
- Create a new feed. In order to help a wikiproject about Mexican Rock music, she filters contributions related to that topic. She keeps such filter at hand to review regularly in the future (and sharing it with her colleagues of the wikiproject). When reviewing contributions, she filters the list further to pay attention to those asking for help to provide them with some advice.
Explored solutions
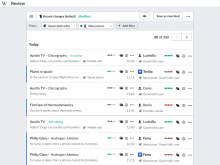
A review feed (such as those listed in T137814) is presented as a list of filtered contributions. Three components are presented (from top to bottom in the mockup):
- Feed management. The current feed is represented with possibilities of manipulation (save a modified feed as a new one, restore the changes, duplicate, etc.) and navigation (i.e., move across feeds).
- Filtering. A feed is represented by a set of filters applied to the general stream of contributions. Users can combine those filters to target a specific subset of contributions. The filtering system is intended to be very flexible (more details on this below).
- List of contributions.
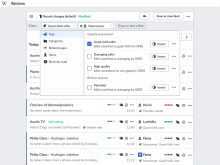
The filter mechanism proposed is intended to be flexible in many ways:
- Aspects to filter. The filter system has been designed to support different categories (and more to be extended in the future). Organised by categories and with the help of autocomplete-like filtering, users can quickly find the filters they want to apply. Based on the filters available in Recent changes, Recent changes linked, and User contributions, the categories explored include: tags (from tools used to create the contribution to ORES-based quality assessments), categories (e.g., articles in your watchlist, a specific category, etc.), related pages (e.g., articles linked from a given one), and users (newcomers, bots, ORES-based assessments for good-faith editors, etc.).
- Search-based criteria. Some of the filtering categories such as categories,not only allow to select a set of predefined options (e.g., categories recently edited by the user), but they allow the user to search for a specific category by typing it.
- Reverse criteria. Filters can be reversed to facilitate excluding a specific group of contributions. for some cases, providing both options explicitly may still be relevant ("bots" and "human editors").
- Visibility control. Filtering normally means to hide what does not meet the filter criteria. However, it is sometimes useful to highlight some elements instead without hiding the rest. In the example, the user has modified the "newcomers" filter to act as a blue highlight for the rows.
- Optimizing for repetition. To encourage exploration it should be easy to go back and forth with the filters. Having a quick access to the recently used filters and allowing to disable filters (in addition to removing them) makes it easy to quickly change the lenses under which reviews are viewed.